Introduction
Background
Syphilis is an infectious disease caused by the spirochete
Treponema pallidum. Syphilis is transmissible by sexual contact with infectious lesions from mother to fetus in utero, via blood product transfusion, and occasionally through breaks in the skin that come into contact with infectious lesions.
Syphilis has a myriad of presentations and can mimic many other infections and immune-mediated processes in advanced stages. Hence, it has earned the nickname "the great impostor." The complex and variable manifestations of the disease prompted Sir William Osler to remark that, "The physician who knows syphilis knows medicine."
Many famous personages throughout history are thought to have suffered from syphilis, including Bram Stoker, Henry VIII, and Vincent Van Gogh. Since the discovery of penicillin in the mid-20th century, the spread of this once very common disease has been largely controlled, but efforts to eradicate the disease entirely have been unsuccessful.
Pathophysiology
T pallidum is a fragile spiral bacterium 6-15 micrometers long by 0.25 micrometers in diameter. Its small size makes it invisible on light microscopy; therefore, it must be identified by its distinctive undulating movements on darkfield microscopy. It can survive only briefly outside of the body; thus, transmission almost always requires direct contact with the infectious lesion.
T pallidum penetrates abraded skin or intact mucous membranes easily and disseminates rapidly, although asymptomatically, via the blood vessels and lymphatics.
Primary syphilis is characterized by the development of a painless chancre at the site of transmission after an incubation period of 3-6 weeks. The lesion has a punched-out base and rolled edges and is highly infectious. It resolves 4-6 weeks after it forms and does not typically leave a scar.
Secondary syphilis develops about 4-10 weeks after the appearance of the primary lesion and has a wide range of presentations. During this stage, the spirochetes multiply and spread throughout the body. Systemic manifestations include malaise, fever, myalgias, arthralgias, lymphadenopathy, and rash. The rash of secondary syphilis typically consists of macular lesions symmetrically distributed over the body and may involve the palms, soles, and oral mucosae. Atypical appearances include papular or even pustular lesions.
Other skin findings of secondary syphilis are condylomata latum and patchy alopecia. Condylomata latum are painless, highly infectious gray-white lesions that develop in warm, moist sites; these are shown in the image below.
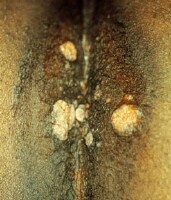
Condylomata lata.
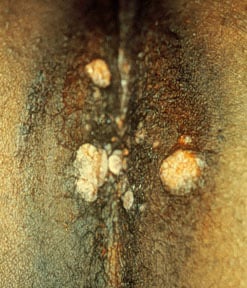
Condylomata lata.
The alopecia is characterized by patchy hair loss of the scalp and facial hair, including the eyebrows. Patients with this finding have been referred to as having a "moth-eaten" appearance. During secondary infection, the immune reaction is at its peak and antibody titers are high.Latent syphilis is a stage at which the features of secondary syphilis have resolved, though patients remain seroreactive. Some patients experience recurrence of the infectious skin lesions of secondary syphilis during this period. About one third of untreated latent syphilis patients go on to develop tertiary syphilis, whereas the rest remain asymptomatic.
Tertiary syphilis develops over months to years and involves slow inflammatory damage to tissues including nerves and blood vessels. The 3 general categories of tertiary syphilis are gummatous syphilis (also called late benign), cardiovascular syphilis, and neurosyphilis.
Gummatous syphilis is characterized by granulomatous lesions, called gummas, which are mainly found in the skin, bones, and liver, but may affect any organ. They may break down and form ulcers, eventually becoming fibrotic. These lesions are noninfectious.
Cardiovascular syphilis occurs at least 10 years after primary infection. The most common manifestation is aneurysm formation in the ascending aorta, caused by chronic inflammatory destruction of the vasa vasorum, the penetrating vessels that nourish the walls of large arteries. Aortic valve insufficiency may result.
Neurosyphilis has several forms. If the spirochete invades the central nervous system (CNS), syphilitic meningitis results. Syphilitic meningitis is an early manifestation, usually occurring within 6 months of the primary infection. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shows high protein, low glucose, high lymphocyte count, and positive syphilis serology.
Meningovascular syphilis occurs as a result of damage to the blood vessels of the meninges, brain, and spinal cord, leading to infarctions causing a wide spectrum of neurologic impairments. Tabes dorsalis develops as the posterior columns and dorsal roots of the spinal cord are damaged. Posterior column impairment results in impaired vibration and proprioceptive sensation, leading to a wide-based gait.
Disruption of the dorsal roots leads to loss of pain and temperature sensation and areflexia. Damage to the cortical regions of the brain leads to general paresis, formerly called "general paresis of the insane," which mimics other forms of dementia. Impairment of memory and speech, personality changes, irritability, and psychotic symptoms develop and may advance to progressive dementia. The Argyll-Robertson pupil, a pupil that does not react to light but does constrict during accommodation, may be seen in tabes dorsalis and general paresis. The precise location of the lesion causing this phenomenon is unknown.
Congenital syphilis, discussed briefly here, is a veritable potpourri of antiquated medical terminology. The treponemes readily cross the placental barrier and infect the fetus, causing a high rate of spontaneous abortion and stillbirth. Within the first 2 years of life, symptoms are similar to severe adult secondary syphilis with widespread condylomata latum and rash. "Snuffles" describes the mucopurulent rhinitis caused by involvement of the nasal mucosae.
Later manifestations of congenital syphilis include bone and teeth deformities including "saddle nose" due to destruction of the nasal septum, "saber shins" due to inflammation and bowing of the tibia, "Clutton's joints" due to inflammation of the knee joints, "Hutchinson's teeth" in which the upper incisors are widely spaced and notched (shown in the image below), and "mulberry molars" in which the molars have too many cusps.
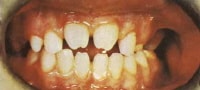
Syphilis. This photograph shows an example of Hutchinson teeth in congenital syphilis. Note notching. Used with permission from Wisdom A. Color Atlas of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Year Book Medical Publishers Inc; 1989.
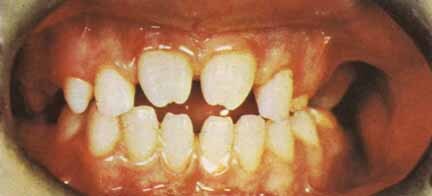
Syphilis. This photograph shows an example of Hutchinson teeth in congenital syphilis. Note notching. Used with permission from Wisdom A. Color Atlas of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Year Book Medical Publishers Inc; 1989.
Tabes dorsalis and general paresis may develop as in adults, with 8th cranial nerve deafness and optic nerve atrophy as well as a variety of other ophthalmologic involvement leading to blindness being additional features.
Frequency
United States
Since reporting began in 1941, the incidence of primary and secondary syphilis in the United States has varied. The incidence dropped from 66.4 cases per 100,000 in 1947 to 3.9 cases per 100,000 in 1956 following the introduction of penicillin, reaching its lowest point ever in 2000 with 2.1 cases per 100,000. Since then, rates have increased again to 2.7 per 100,000 in 2004, primarily due to an increased incidence amongst men who have sex with men (MSM).
1 International
Internationally, the prevalence of syphilis varies by region, the highest rates being in South and Southeast Asia, followed closely by sub-Saharan Africa. The third highest rates are in the regions of Latin America and the Caribbean.
2 Mortality/Morbidity
The morbidity and mortality of untreated syphilis must be estimated from the limited data available regarding its natural course. These data are largely from one retrospective study of autopsies and two prospective studies, most notably the famous Tuskegee Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male, which fell under serious ethical scrutiny in later years for exploiting a vulnerable patient population and not offering treatment for the disease when it became available after the study was underway. These data indicate that approximately one third of patients left untreated will develop late complications, with 10% of the total developing cardiovascular syphilis; 6%, neurosyphilis; and 16%, gummatous syphilis. Mortality rates in general are greater among those affected, and late complications appear to occur more commonly in men than in women.
3,4 Race
Racial disparities exist, with blacks affected more frequently than whites. In 2004, the rate among blacks was 5.6 times higher than the rate among whites.
1 Sex
Men are affected more frequently with primary or secondary syphilis than women. The male-to-female ratio is 5.9.
1 In 2007, 65% of of new cases occurred in men who have sex with men, and there is a high rate of HIV co-infection.
5 Age
In 2007, the rate of primary and secondary syphilis was highest in people aged 25-29 years (8.9 per 100,000).
5 Clinical
History
Because the manifestations of syphilis (particularly advanced syphilis) are nonspecific and may masquerade as many other diseases, the physician must keep a high index of suspicion regarding the possible diagnosis of syphilis.
The clinician should carefully reconstruct the time course and description of all symptoms and lesions and obtain a complete sexual history including history of STDs, condom use, and the number and gender of previous sexual partners.
The United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) issued screening guidelines to include all pregnant women and people at risk of acquiring syphilis.
The US Preventive Services Task Force has reaffirmed its recommendation for screening all pregnant women for syphilis infection at the first prenatal visit. High-risk women (eg, uninsured women, women living in poverty, sex workers, illicit drug users, those with other sexually transmitted diseases including HIV, those living in communities with high syphilis incidence) should also be tested in the third trimester of pregnancy and at delivery. If test results are positive for syphilis, the treatment of choice is parenteral benzathine penicillin G. Dosage and length of treatment depend on the stage and clinical manifestations of the disease.
6 - Primary syphilis
- Genital chancre - Frequently solitary, may be multiple (Sometimes seen as "kissing" lesions on opposing skin surfaces, for example, the labia. This is shown in the image below.)
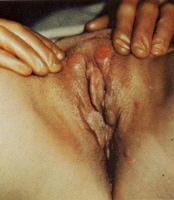
Syphilis. This photograph depicts primary syphilis "kissing" lesions. Used with permission from Wisdom A. Color Atlas of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Year Book Medical Publishers Inc; 1989.
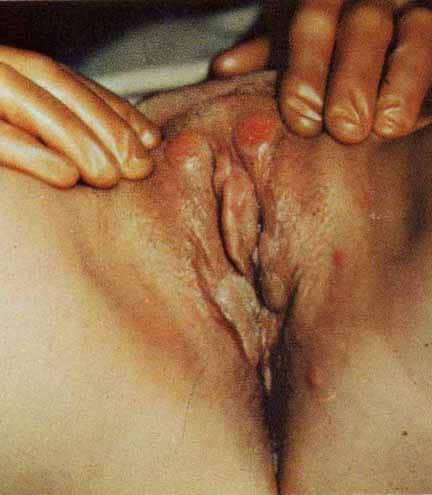
Syphilis. This photograph depicts primary syphilis "kissing" lesions. Used with permission from Wisdom A. Color Atlas of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Year Book Medical Publishers Inc; 1989.
- A chancre appears 3-6 weeks after initial sexual contact.
- Secondary syphilis
- Rash - Nonpruritic and bilaterally symmetrical
- Patchy alopecia
- Condylomata latum, shown in the image below
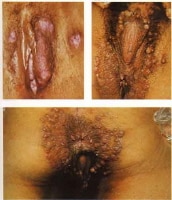
These photographs illustrate examples of condylomata lata. The lesions resemble genital warts (condylomata acuminata). Fluids exuding from these lesions are highly infectious. Used with permission from Wisdom A. Color Atlas of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Year Book Medical Publishers Inc; 1989.
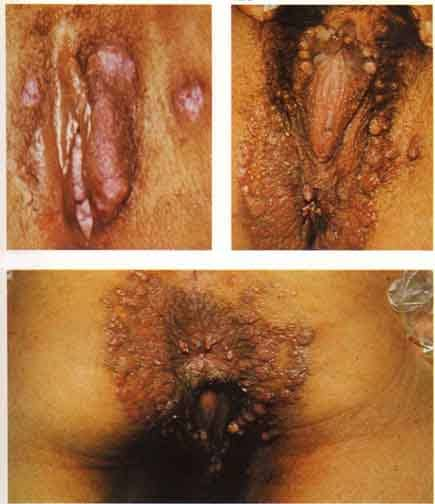
These photographs illustrate examples of condylomata lata. The lesions resemble genital warts (condylomata acuminata). Fluids exuding from these lesions are highly infectious. Used with permission from Wisdom A. Color Atlas of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Year Book Medical Publishers Inc; 1989.
- Constitutional symptoms of secondary syphilis include malaise, sore throat, headache, fever, anorexia, and, rarely, meningismus.
- Tertiary syphilis
- Altered mental status
- Focal neurologic findings, including sensorineural hearing and vision loss
- Dementia
- Patients may have symptoms related to the cardiovascular or central nervous systems.
Physical
Conduct the physical examination with the manifestations of primary, secondary, and tertiary syphilis in mind. The lesions and exanthem of primary and secondary syphilis are infectious; thus, gloves and other relevant personal protective equipment must be worn.
- Primary syphilis
- The chancre of primary syphilis usually begins as a single, painless papule that rapidly becomes eroded and indurated. The ulcer has a cartilaginous consistency at the edge and base. A lesion is shown in the image below.
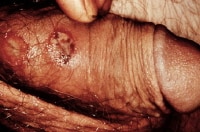
Syphilitic chancre.
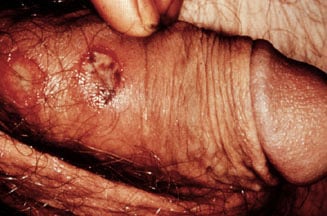
Syphilitic chancre.
- Chancres usually are located on the penis in heterosexual men, but, in homosexual men, they may be found in the anal canal, mouth, or external genitalia. Common primary sites in women include the cervix and labia.
- Atypical primary lesions are common and may manifest as a papular lesion without subsequent ulceration or induration.
- The primary lesion usually is associated with regional lymphadenopathy that may be unilateral or bilateral. Inguinal adenitis is usually discrete, firm, mobile, and painless, without overlying skin changes.
- Secondary syphilis
- Secondary syphilis may present in many different ways but usually includes a localized or diffuse mucocutaneous rash and generalized nontender lymphadenopathy. The exanthem may be macular, papular, pustular, or mixed.
- Typical early lesions are usually less than (20 size or number), round, discrete, nonpruritic, and symmetric macules distributed on the trunk and proximal extremities. Red papular lesions also may appear on the palms, soles, face, and scalp and may become necrotic. Patchy and nonpatchy alopecia may occur. In intertriginous areas, papules may coalesce to form highly infectious lesions called condylomata lata. Lesions usually progress from red, painful, and vesicular to "gun metal grey" as the rash resolves. Examples of the rash are shown in the images below.
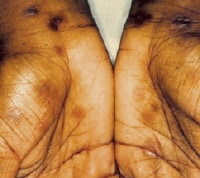
Secondary syphilis - Exanthem.
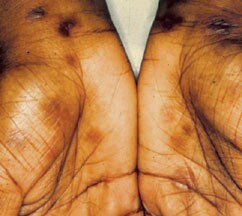
Secondary syphilis - Exanthem.
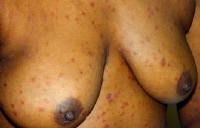
Secondary syphilis - Exanthem.
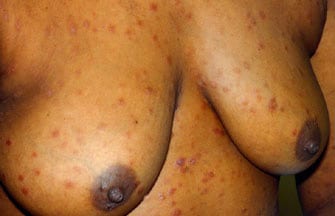
Secondary syphilis - Exanthem.
- Mucous patches are superficial mucosal erosions, usually painless, that may develop on the tongue, oral mucosa, lips, vulva, vagina, and penis.
- Other, less common manifestations of secondary syphilis include gastrointestinal involvement, hepatitis, nephropathy, proctitis, arthritis, and optic neuritis.
- Tertiary syphilis
- Symptomatic tertiary syphilis is the result of a chronic, progressive inflammatory process that eventually produces clinical symptoms years to decades after the initial infection.
- Gummatous syphilis manifests as coalescent granulomatous lesions that usually affect skin, bone, and mucous membranes but may involve any organ system. The lesions often cause local destruction of the affected organ system. Gummas in tertiary syphilis are shown in the image below.
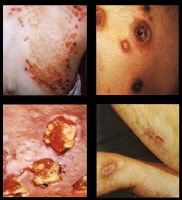
Syphilis. These photographs show close-up images of gummas observed in tertiary syphilis. Used with permission from Wisdom A. Color Atlas of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Year Book Medical Publishers Inc; 1989.
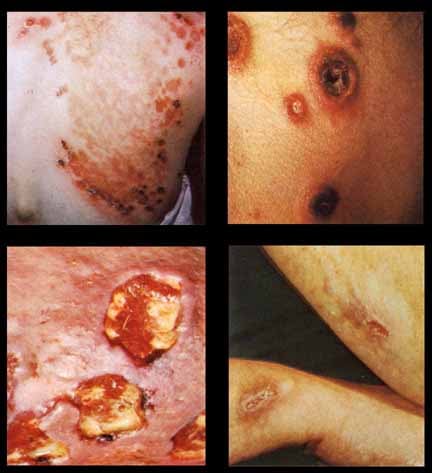
Syphilis. These photographs show close-up images of gummas observed in tertiary syphilis. Used with permission from Wisdom A. Color Atlas of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Year Book Medical Publishers Inc; 1989.
- Cardiovascular syphilis results from endarteritis of the aorta, subsequent medial necrosis, aortitis, and aneurysm formation. Other large arteries may be affected as well.
- Neurosyphilis may be asymptomatic or symptomatic. In asymptomatic neurosyphilis, no signs or symptoms are present, but CSF abnormalities are demonstrable, including possible pleocytosis, elevated protein, decreased glucose, or a reactive CSF Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test.
- Symptomatic neurosyphilis may manifest as syphilitic meningitis, meningovascular syphilis, or parenchymatous neurosyphilis.
- Syphilitic meningitis usually develops within 6 months to several years of initial infection, and patients present with typical symptoms of meningitis, including headache, nausea and vomiting, and photophobia, but are typically afebrile. Patients may exhibit cranial nerve abnormalities.
- Meningovascular syphilis manifests 5-10 years after infection and is the result of endarteritis, which affects small blood vessels of the meninges, brain, and spinal cord. Patients may present with CNS vascular insufficiency or outright stroke.
- Parenchymatous neurosyphilis results from direct parenchymal CNS invasion by T pallidum and is usually a late development (15-20 years after primary infection).
- Patients present with ataxia; incontinence; paresthesias; and loss of position, vibratory, pain, and temperature sensations. Paresis and dementia, with changes in personality and intellect, may develop.











 The necessity of wearing dental braces and the treatment duration should be determined by the orthodontist. All personal factors and specifics should be taken into account when making a decision about how long a patient should wear dental braces. Usually, an average period of treatment for children does not exceed 2-3 years, with 6 months of minimal time of wearing orthodontic braces. Braces do not cause pain but sometimes there can be an uncomfortable feeling in your mouth. While wearing dental braces, you need to see orthodontist once per month.
The necessity of wearing dental braces and the treatment duration should be determined by the orthodontist. All personal factors and specifics should be taken into account when making a decision about how long a patient should wear dental braces. Usually, an average period of treatment for children does not exceed 2-3 years, with 6 months of minimal time of wearing orthodontic braces. Braces do not cause pain but sometimes there can be an uncomfortable feeling in your mouth. While wearing dental braces, you need to see orthodontist once per month. The experiments involved 58 participants, 29 of which had lip piercing. The doctors used several approaches to measure their gum recession, and it turned out that those, who have no lip piercing have about 33% lower chances to have receding gums on their bottom front teeth. At that, other estimations showed that the longer a person has lip piercing, the higher chances he or she has to have problems with bottom front teeth. For example, those who have lip piercing for 36 months have 80% higher chances to have gum recession.
The experiments involved 58 participants, 29 of which had lip piercing. The doctors used several approaches to measure their gum recession, and it turned out that those, who have no lip piercing have about 33% lower chances to have receding gums on their bottom front teeth. At that, other estimations showed that the longer a person has lip piercing, the higher chances he or she has to have problems with bottom front teeth. For example, those who have lip piercing for 36 months have 80% higher chances to have gum recession.

























